Quantifying London Traffic Dynamics for Air Pollution Estimation
Open-source library to automate collection of live traffic video data and extraction of descriptive traffic statistics. 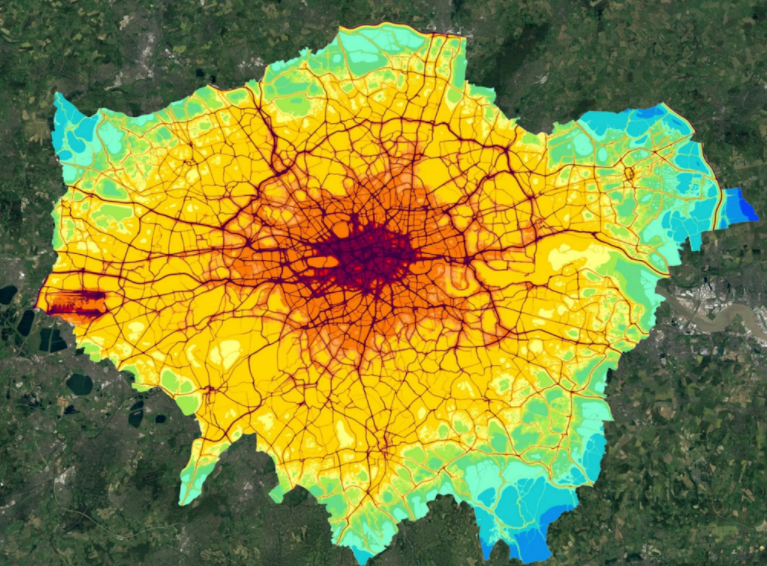 Read more
Read more
Open-source library to automate collection of live traffic video data and extraction of descriptive traffic statistics.  Read more
Read more
Published in Harvard Data Science Review, 2020
We investigate the COMPAS model—a black-box recidivism prediction model used widely in America’s justice system. Read more
Recommended citation: Cynthia Rudin, Caroline Wang, and Beau Coker (2020). "The age of secrecy and unfairness in recidivism prediction." HDSR. 2(1).
Published in Harvard Data Science Review, 2020
A rejoinder to, “The age of secrecy and unfairness in criminal recidivism prediction”. Read more
Recommended citation: Cynthia Rudin, Caroline Wang, Beau Coker (2020). "Broader issues surrounding model transparency in criminal justice risk scoring." HDSR. 2(1).
Published in Journal of Quantitative Criminology, 2022
We design various interpretable machine learning models to predict criminal recidivism. Read more
Recommended citation: Caroline Wang*, Bin Han*, Bhrij Patel, Feroze Mohideen, Cynthia Rudin (2022). "In pursuit of interpretable, fair and accurate machine learning for criminal recidivism prediction." Journal of Quantitative Criminology.
Published in AAAI, 2023
We propose DM$^2$, an algoritm that allows a team of agents to perform cooperative tasks by independently imitating corresponding experts agents from a team of experts. Read more
Recommended citation: Caroline Wang*, Ishan Durugkar*, Elad Liebman*, Peter Stone. "DM$^2$: Distributed Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning via Distribution Matching." AAAI 2023.
Published in AAMAS, 2023
TLDR: We propose D-Shape, an RL+IL algorithm that allows learning from suboptimal demonstrations while retaining the ability to find the optimal policy with respect to the task reward. Read more
Recommended citation: Caroline Wang, Garrett Warnell, Peter Stone (2023). "D-Shape: Demonstration Shaped Reinforcement Learning." AAMAS 2023.
Published in AAAI, 2024
We introduce Causal Bisimulation Learning (CBM), a method that learns the causal relationships in the dynamics and reward functions for each task to derive a minimal, task-specific abstraction. Read more
Recommended citation: Zizhao Wang*, Caroline Wang*, Xuesu Xiao, Yuke Zhu, Peter Stone (2024). "Building Minimal and Reusable Causal State Abstractions for Reinforcement Learning." AAAI 2024.
Published in NeurIPS, 2024
Existing paradigms for multi-agent coordination are limited by assuming that either all agents are controlled (e.g. the typical cooperative MARL algorithm), or that only a single agent is controlled (ad hoc teamwork / zero shot coordination). We pose the N-Agent Ad Hoc Teamwork (NAHT) problem to the community, to lift these restrictions and pave the path towards more open multi-agent learning paradigms. Read more
Recommended citation: Caroline Wang, Arrasy Rahman, Ishan Durugkar, Elad Liebman, Peter Stone. "N-Agent Ad Hoc Teamwork." NeurIPS 2024.
Published in CoCoMARL Workshop at RLC, 2025
We formulate ad hoc teamwork as an open-ended learning process between a regret-maximizing teammate generator and an ad hoc teamwork agent. Read more
Recommended citation: Caroline Wang, Arrasy Rahman, Jiaxun Cui, Yoonchang Sung, Peter Stone. "ROTATE: Regret-Driven Open-ended Training for Ad Hoc Teamwork." CoCoMARL Workshop at RLC 2025. https://openreview.net/forum?id=2WW5SXXHn4
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown! Read more
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field. Read more
Undergraduate course, University 1, Department, 2014
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post. Read more
Workshop, University 1, Department, 2015
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post. Read more